Encryption
On this website, we explain what you should encrypt and how you can easily encrypt individual files and folders.
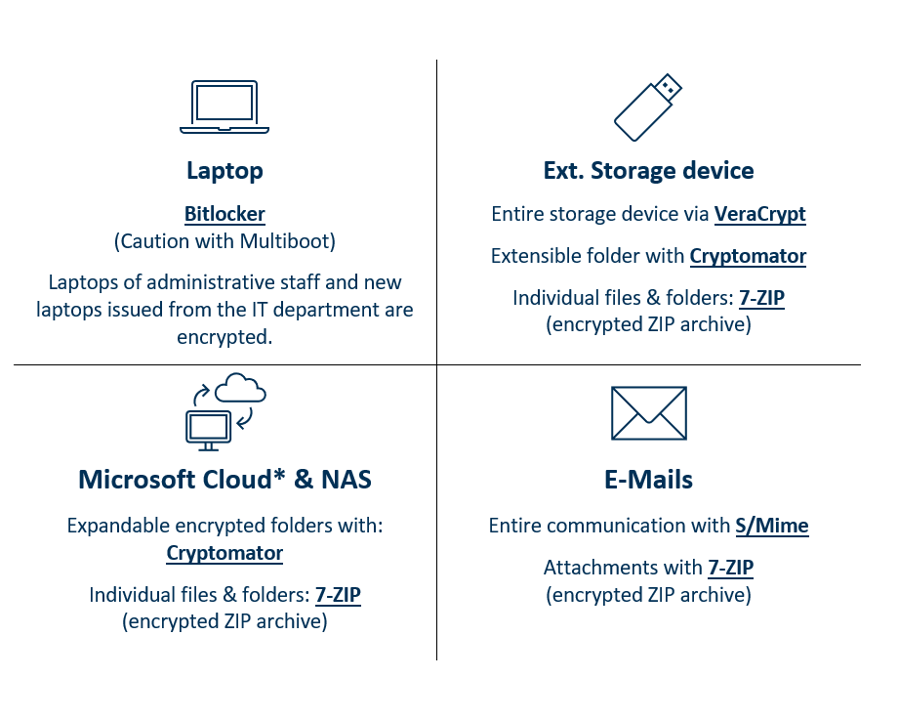
Why and how to encrypt?
Computer
Reasons for encrypting
Here you store all your data for your daily work. If your computer is stolen or gets lost, others can access all your data by removing the hard drive.
If you order a computer via the University IT and/
or have the University IT setting up your computer the employees of the University IT encrypt the hard drives for you (from November onwards – more details here). Apple and Linux:
- In order to encrypt an apple device please use FileVault for encryption.
- Due to the large number of different Linux distributions, there are no standardized instructions that are suitable for all Linux systems. As a rule, widely used distributions (such as Ubuntu) support the encryption of hard disks with LUKS (cryptsetup). Please inquire which variant is provided by your distribution.
Windows hard drive encryption with Bitlocker:
The hard drives of computers with Windows as operating system can be encrypted with BitLocker.
If you are not sure whether or not your hard drives are encrypted, you can check this by going to “Control Panel\System and Security\BitLocker-network encryption”. If one or several hard drive(s) are not encrypted, you can enable BitLocker for these hard drives. Please refer to the instructions for more information. If you need more help, please contact your administrator or the IT support.
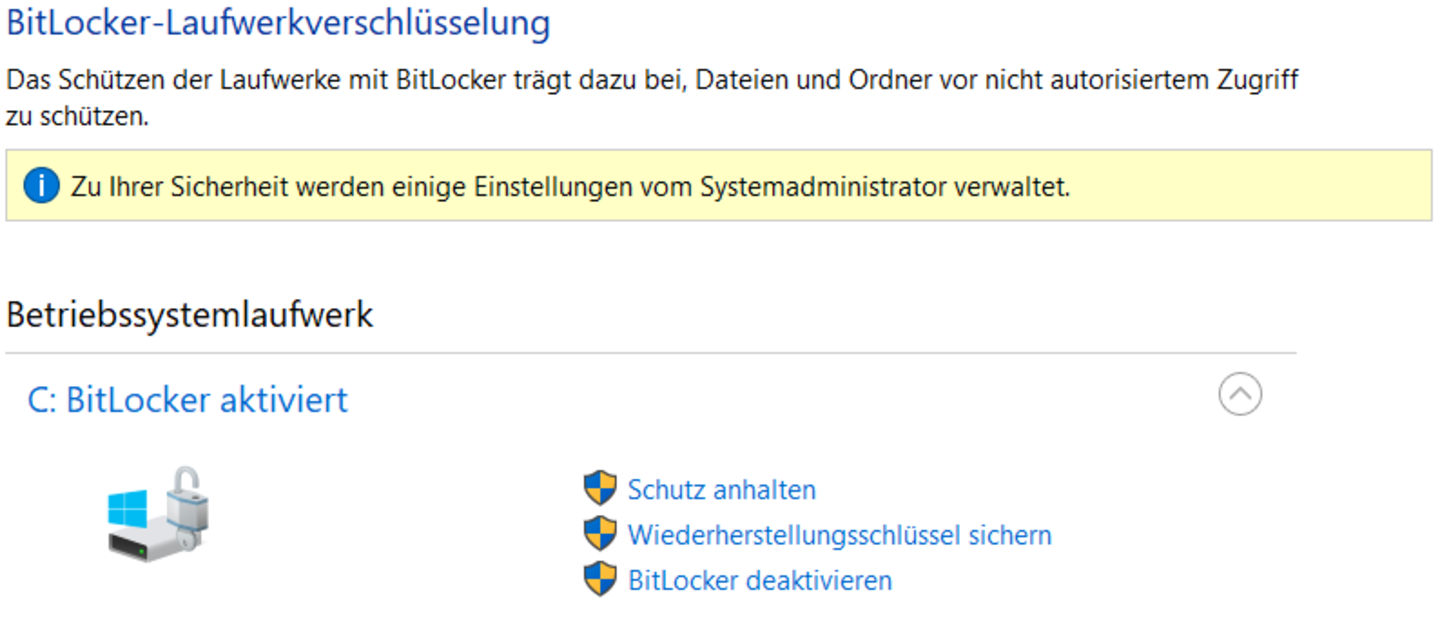 Credit: Informationssicherheitsteam
Credit: InformationssicherheitsteamOverview of the Bitlocker hard drive encryption External storage devices
Reasons for encrypting
External storage devices, such as USB sticks, SD cards or hard drives are popular for storing or exchanging information. However, they can easily get lost or be stolen. In addition, most external storage devices do not allow for the complete deletion of the data.
Encrypting the entire storage device with VeraCrypt:
If you want to encrypt the entire storage device, you can use VeraCrypt to do so. Please note that admin rights are required for installing and encrypting the storage device.
Click here for an instruction on encrypting with VeraCrypt.
Creating an expandable encrypted folder with Cryptomator:
You can use Cryptomator to store an encrypted folder on the storage device. The benefit of this folder is that files can be modified, added or deleted at any time. We have created Cryptomator instructions that can be found in our information material.
Encrypting individual folders and files with a ZIP archive:
If you want to encrypt individual files or folders which you no longer need to edit, you can use an encrypted ZIP archive to do so. Just follow the steps in the instructions and copy the encrypted zip archive on the storage device.
E-mails
Reasons for encrypting
Sending e-mails is the most popular way of professional communication. However, it is not widely known that sending an e-mail can be compared to sending a postcard. With minimal effort, it is possible for anybody to read the content of an e-mail that is not encrypted.
Encrypting the entire e-mail communication with S/
MIME: By using the S/
MIME encryption, e-mails can be sent securely. A digital certificate is needed. The certificate is special type of file linked to a password that has to be stored on your computer. In order to read encrypted e-mails, you need the certificate including your password. The request form and more information on the certificate, can be found here.
Encrypting attachments by using ZIP archives:
Encrypting attachments by using ZIP archives:
However, you do not need S/
MIME to protect individual attachments you want to send by using an encrypted ZIP archive. Please do not send the password for the ZIP archive via e-mail but use another way (e.g. in person, via phone or letter) to disclose the password. For detailed instructions on how to create encrypted ZIP archives, please refer to our information material.
Network drives of the University of Mannheim (NAS)
Reasons for encrypting
Network drives are popular means for storing and exchanging data. We also recommend using the internal network drives of the university. However, most users do not know who is authorized to access the network drive and thus allowed to read or even copy the data stored there.
Creating an expandable encrypted folder with Cryptomator:
You can use Cryptomator to store an encrypted folder on the storage device. The benefit of this folder is that files can be modified, added or deleted at any time. We have created Cryptomator instructions that can be found in our information material.
Encrypting individual folders and files with a ZIP archive:
Individual folders or files can be protected by using an encrypted ZIP archive (click here for instructions) and store it on the network drive. However, such an archive cannot be expanded. It is therefore best to store only final files in zip archives.
Microsoft Cloud (OneDrive, Teams & OneNote)
Reasons for encrypting
The University of Mannheim uses Office 365, which means that all employees and doctoral students can use the Microsoft Cloud. Microsoft Cloud includes OneDrive, SharePoint, Teams and OneNote.
When processing data in the Microsoft cloud, it is mandatory to handle the information contained in the documents carefully. Administrative data classified as TLP white are the only data that may be stored in the cloud. For more information, please refer to the terms of use for the M 365 Cloud Services.
Creating an expandable encrypted folder with Cryptomator:
You can use Cryptomator to store an encrypted folder in the cloud. The benefit of this folder is that files can be modified, added or deleted at any time. If you use a jointly encrypted folder, it is not possible to simultaneously work on the files in this folder.
We have created Cryptomator instructions that can be found in our information material.
Encrypting individual folders and files with a ZIP archive:
Individual folders or files can be protected by using an encrypted ZIP archive (click here for instructions) and store it in the cloud. However, such an archive cannot be expanded.
Other cloud services
Reasons for encrypting
Cloud services, such as iCloud, DropBox or GoogleDrive, are becoming more and more popular and seem to be an easy alternative for exchanging data. However, you can never be sure how the service provider handles the data stored there and who is able to access the data.
Therefore, the information security team advises you to not use these services for work purposes.
Creating an expandable encrypted folder with Cryptomator:
You can use Cryptomator to store an encrypted folder in the cloud. The benefit of this folder is that files can be modified, added or deleted at any time. If you use a jointly encrypted folder, it is not possible to simultaneously work on the files in this folder.
We have created Cryptomator instructions that can be found in our information material.
Encrypting individual folders and files with a ZIP archive:
Individual folders or files can be protected by using an encrypted ZIP archive (click here for instructions) and store it in the cloud. However, such an archive cannot be expanded.

More information on encryption
How does it work? How can I ensure that the communication is encrypted and secure?
Types of encryption
Symmetric encryption
Symmetric encryption means that a key is used for the encryption and decryption process. The text is encrypted with a key and the secret text so generated is being transmitted to the recipient who will then use the same key to decrypt the secret text. The problem with this kind of encryption is transmitting the key. The key needs to be exchanged in a secure way. If someone knows the key, they can also decrypt the secret text.
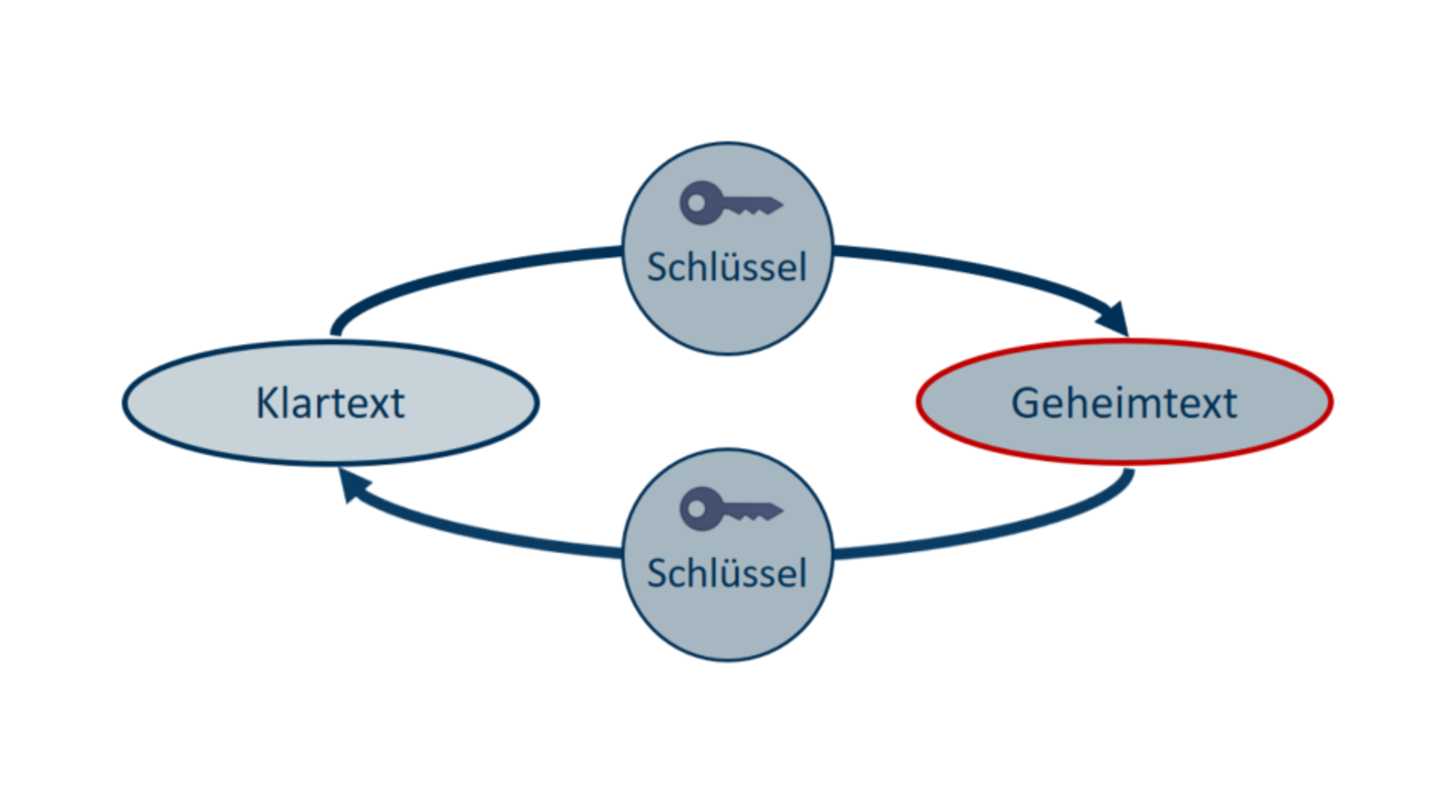 Credit: Informationssicherheitsteam
Credit: InformationssicherheitsteamAsymmetric encryption
In contrast to symmetric encryption, where you have one key for encryption and decryption, asymmetric encryption means that there are two keys. A private key and a public key.
As you can see, the text is encrypted with the public key and decrypted with the private key. It is not necessary to find a secure way to exchange the key, since the public key is publicly available. Anybody who has the recipient’s public key can use this key to encrypt a message. The recipient can then use their private key to decrypt the text.
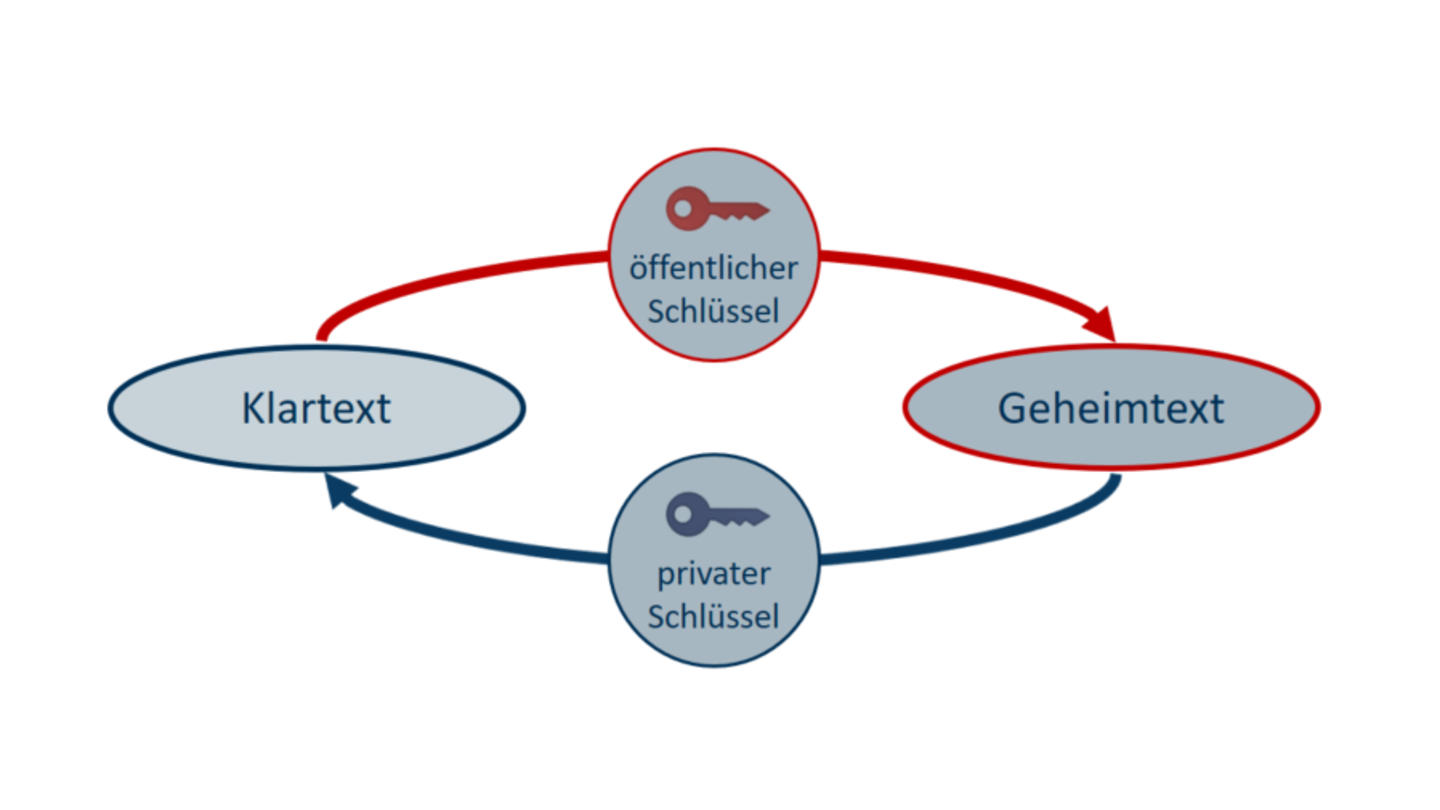 Credit: Informationssicherheitsteam
Credit: InformationssicherheitsteamSecure communication
Websites
Make sure that your communication with the website is encrypted, when browsing and in particular when entering confidential information, such as your password. The lock symbol in the address field of your browser indicates that your communication with the website is encrypted.
 Credit: Informationssicherheitsteam
Credit: InformationssicherheitsteamEncrypted communication in Firefox  Credit: Informationssicherheitsteam
Credit: InformationssicherheitsteamEncrypted communication in Chrome  Credit: Informationssicherheitsteam
Credit: InformationssicherheitsteamEncrypted communication in Edge Messenger services
There are many messenger services, such as WhatsApp, Skype or Signal. More and more of these services are offering encrypted communication. At the first glance, it is difficult to determine how secure this communication really is. When choosing a messenger service, please make sure that this service uses end-to-end encryption and that this service is open-source . Open-source means that the source code can be accessed by anybody and experts can search the code for security gaps.
However, you should refrain from using such messenger services for work purposes.
Wireless Access
When using the wireless, please make sure that it is WPA2 encrypted.
If you are using a foreign or public network, e.g., wireless at a hotel, please use only encrypted connections such as HTTPS. If you process internal information of the university, please enable the VPN connection to the university’s network.
